Leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Competitive Intelligence (CI) Research
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24883/eagleSustainable.v15i.469Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Large Language Models (LLMs), Scholarly Research, Competitive Intelligence (CI), GPT ModelsAbstract
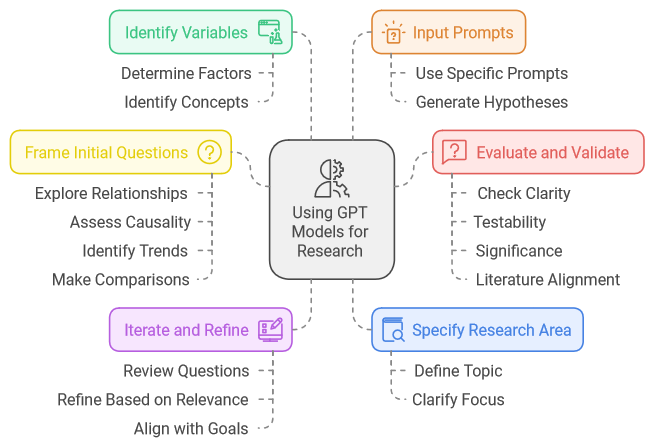
Objective: The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly influenced research and academic practices, prompting universities to create guidelines for student use of large language models (LLMs). However, there is ongoing debate among academic journals and conferences regarding the necessity of reporting AI assistance in manuscript development. This paper aims to explore diverse perspectives on the use of LLMs in scholarly research, particularly within the context of competitive intelligence (CI), and to offer guidelines for CI researchers on how to effectively leverage AI tools like GPT models.
Method: The study conducts a comprehensive review of existing literature on the integration of AI in academic research, focusing specifically on the capabilities of generative AI models such as ChatGPT-4, Scholar GPT, and Consensus GPT. These models, developed by OpenAI, are evaluated for their utility in various stages of the research process, including literature review, qualitative analysis, and data analysis. The analysis emphasizes how the quality of AI-generated outputs depends on the specificity of the user's input.
Results: While LLMs have demonstrated significant potential in enhancing literature reviews, qualitative research, and data analysis, the study finds that their full capabilities in academic research remain underexplored. The research highlights both the concerns about potential "contamination" of scholarly work through AI use and the benefits these models offer, especially when used strategically.
Conclusions: The article presents a structured guide for business researchers, with particular emphasis on those engaged in competitive intelligence, to integrate AI language models effectively throughout the research process. The findings underline the importance of input specificity and provide practical recommendations for leveraging LLMs to enhance research efficiency and output quality.
Downloads
References
Atkinson, C. F. (2024). Cheap, quick, and rigorous: Artificial intelligence and the systematic literature review. Social Science Computer Review, 42(2), 376-393. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/08944393231196281
Bang, Y., Cahyawijaya, S., Lee, N., Dai, W., Su, D., Wilie, B., ... & Fung, P. (2023). A multitask, multilingual, multimodal evaluation of chatgpt on reasoning, hallucination, and interactivity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2023.ijcnlp-main.45
Bostrom, N. and Yudkowsky, E. (2018), “The ethics of artificial intelligence”, in Artificial Intelligence Safety and Security, Chapman and Hall/CRC, pp. 57-69. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781351251389-4
Boyd, A. (2023, October). Higher Ed Grapples with AI's Impact. Voltedu. Retrieved from https://voltedu.com/education-administration/higher-ed-grapples-with-ais-impact/
Brand, J., Israeli, A., & Ngwe, D. (2023). Using gpt for market research. Available at SSRN 4395751. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4395751
Budhwar, P., Chowdhury, S., Wood, G., Aguinis, H., Bamber, G. J., Beltran, J. R., ... & Varma, A. (2023). Human resource management in the age of generative artificial intelligence: Perspectives and research directions on ChatGPT. Human Resource Management Journal, 33(3), 606-659. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12524
Burger, B., Kanbach, D. K., Kraus, S., Breier, M., & Corvello, V. (2023). On the use of AI-based tools like ChatGPT to support management research. European Journal of Innovation Management, 26(7), 233-241. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/EJIM-02-2023-0156
Butson, R., & Spronken-Smith, R. (2024). AI and its implications for research in higher education: a critical dialogue. Higher Education Research & Development, 43(3), 563-577. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2023.2280200
Chen, Y., Andiappan, M., Jenkin, T., & Ovchinnikov, A. (2023). A Manager and an AI Walk into a Bar: Does ChatGPT Make Biased Decisions Like We Do?. Available at SSRN 4380365. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4380365
Ciechanowski, L., Jemielniak, D., & Gloor, P. A. (2020). TUTORIAL: AI research without coding: The art of fighting without fighting: Data science for qualitative researchers. Journal of Business Research, 117, 322-330. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.06.012
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage publications.
Dwivedi, Y.K., Kshetri, N., Hughes, L., Slade, E.L., Jeyaraj, A., Kar, A.K., Baabdullah, A.M., Koohang, A., Raghavan, V., Ahuja, V., Albanna, A., Albashrawi, M.A., Al-Busaidi, A.S., Balakrishnan, J., Barlette, Y., Basu, S., Bose, I., Brooks, L., Buhalis, D., Carter, L., Chowdhury, S., Crick, T., Cunningham, S.W., Davies, G.H., Davison, R.M., De, R., Dennehy, D., Duan, Y., Dubey, R., Dwivedi, R., Edwards, J.S., Flavian, C., Gauld, R., Grover, V., Hu, M.C., Janssen, M., Jones, P., Junglas, I., Khorana, S., Kraus, S., Larsen, K.R., Latreille, P., Laumer, S., Malik, T.F., Mardani, A., Mariani, M., Mithas, S., Mogaji, E., Horn Nord, J., O’Connor, S., Okumus, F., Pagani, M., Pandey, N., Papagiannidis, S., Pappas, I.O., Pathak, N., Pries-Heje, I., Raman, R., Rana, N.P., Volker Rehm, S., Ribeiro-Navarrete, S., Richter, A., Rowe, F., Sarker, S., Carsten Stahl, B., Tiwari, M.K., van der Aalst, W., Venkatesh, V., Viglia, G., Wade, M., Walton, P., Wirtz, J. and Wright, R. (2023), “‘So what if ChatGPT wrote it?’ Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy”, International Journal of Information Management, Vol. 71, 102642, doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2023.102642. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2023.102642
Garcia, M. B. (2024). Using AI tools in writing peer review reports: should academic journals embrace the use of ChatGPT?. Annals of biomedical engineering, 52(2), 139-140. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03299-7
Giray, L. (2023). Prompt engineering with ChatGPT: a guide for academic writers. Annals of biomedical engineering, 51(12), 2629-2633. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03272-4
Girotra, K., Meincke, L., Terwiesch, C., & Ulrich, K. T. (2023). Ideas are dimes a dozen: Large language models for idea generation in innovation. Available at SSRN 4526071. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4526071
Golan, R., Reddy, R., Muthigi, A., & Ramasamy, R. (2023). Artificial intelligence in academic writing: a paradigm-shifting technological advance. Nature reviews urology, 20(6), 327-328. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-023-00746-x
Gray, A. (2024). ChatGPT" contamination": estimating the prevalence of LLMs in the scholarly literature. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.16887.
Grossmann, I., Feinberg, M., Parker, D. C., Christakis, N. A., Tetlock, P. E., & Cunningham, W. A. (2023). AI and the transformation of social science research. Science, 380(6650), 1108-1109. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adi1778
Hamilton, L., Elliott, D., Quick, A., Smith, S., & Choplin, V. (2023). Exploring the use of AI in qualitative analysis: A comparative study of guaranteed income data. International journal of qualitative methods, 22, 16094069231201504. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069231201504
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2019). Multivariate data analysis, (8th ed.). London: U.K., Cengage Learning.
Hassani, H., & Silva, E. S. (2023). The role of ChatGPT in data science: how ai-assisted conversational interfaces are revolutionizing the field. Big data and cognitive computing, 7(2), 62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7020062
Khalifa, M., & Albadawy, M. (2024). Using artificial intelligence in academic writing and research: An essential productivity tool. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Update, 100145. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpbup.2024.100145
Kesting, P. (2024). How artificial intelligence will revolutionize management studies: a Savagean perspective. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 40(2), 101330. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scaman.2024.101330
Khlaif, Z. N., Mousa, A., Hattab, M. K., Itmazi, J., Hassan, A. A., Sanmugam, M., & Ayyoub, A. (2023). The potential and concerns of using AI in scientific research: ChatGPT performance evaluation. JMIR Medical Education, 9, e47049. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2196/47049
Knopp, M. I., Warm, E. J., Weber, D., Kelleher, M., & others. (2023). AI-Enabled Medical Education: Threads of Change, Promising Futures, and Risky Realities Across Four Potential Future Worlds. JMIR Medical Education, 2023(1). https://mededu.jmir.org/2023/1/e50373 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2196/50373
Lund, B. D., & Wang, T. (2023). Chatting about ChatGPT: how may AI and GPT impact academia and libraries?. Library hi tech news, 40(3), 26-29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/LHTN-01-2023-0009
Meskó, B. (2023). Prompt engineering as an important emerging skill for medical professionals: tutorial. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 25, e50638. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2196/50638
Miller, J. P. (2012). Millennium Intelligence: Understanding and Conducting Competitive Intelligence in the Digital Age. Journal of Sustainable Competitive Intelligence, 2(2). https://doi.org/10.24883/IberoamericanIC.v2i2.42
Mouton, J., & Marais, H. C. (1988). Basic concepts in the methodology of the social sciences. Hsrc Press.
Nguyen-Trung, K., Saeri, A. K., & Kaufman, S. (2023). Applying ChatGPT and AI-powered tools to accelerate evidence reviews. DOI: 10.31219/osf.io/pcrqf DOI: https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/pcrqf
OpenAI. (2024). ChatGPT (4.0 version) [Large multimodal model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
Park, Y. J., Kaplan, D., Ren, Z., Hsu, C. W., Li, C., Xu, H., ... & Li, J. (2024). Can ChatGPT be used to generate scientific hypotheses?. Journal of Materiomics, 10(3), 578-584. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2023.08.007
Perkins, M., & Roe, J. (2023). Academic publisher guidelines on AI usage: A ChatGPT supported thematic analysis. F1000Research, 12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.142411.1
Rahman, M., Terano, HJR, Rahman, N., Salamzadeh, A., Rahaman, S.(2023). ChatGPT and Academic Research: A Review and Recommendations Based on Practical Examples. Journal of Education, Management and Development Studies, 3(1), 1-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.52631/jemds.v3i1.175
Rane, N. L., Tawde, A., Choudhary, S. P., & Rane, J. (2023). Contribution and performance of ChatGPT and other Large Language Models (LLM) for scientific and research advancements: a double-edged sword. International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science, 5(10), 875-899.
Rocha, I., & Lopes, L. L. S. (2023). The Process of Implementing Competitive Intelligence in a Service Organization. Journal of Sustainable Competitive Intelligence, 13, e0438. https://doi.org/10.24883/IberoamericanIC.v13i.438 DOI: https://doi.org/10.24883/IberoamericanIC.v13i.438
Sabol, M., Hair, J., Cepeda, G., Roldán, J. L., & Chong, A. Y. L. (2023). PLS-SEM in information systems: seizing the opportunity and marching ahead full speed to adopt methodological updates. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 123(12), 2997-3017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-07-2023-0429
Sarstedt, M., Adler, S. J., Rau, L., & Schmitt, B. (2024). Using large language models to generate silicon samples in consumer and marketing research: Challenges, opportunities, and guidelines. Psychology & Marketing. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21982
Scopus. (2024). CiteScore metrics for Top 10% Journals: 5.3. Retrieved from https://www.scopus.com/sources.uri
Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research, 104, 333-339. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039
Vaid, S., Puntoni, S., & Khodr, A. (2023). Artificial intelligence and empirical consumer research: A topic modeling analysis. Journal of Business Research, 166, 114110. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.114110
Van Dis, E. A., Bollen, J., Zuidema, W., Van Rooij, R., & Bockting, C. L. (2023). ChatGPT: five priorities for research. Nature, 614(7947), 224-226. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-00288-7
Wang, M., Wang, M., Xu, X., Yang, L., Cai, D., & Yin, M. (2023). Unleashing ChatGPT's Power: A Case Study on Optimizing Information Retrieval in Flipped Classrooms via Prompt Engineering. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2023.3324714
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms: the author(s) authorize(s) the publication of the text in the journal;
2. The author(s) ensure(s) that the contribution is original and unpublished and that it is not in the process of evaluation by another journal;
3. The journal is not responsible for the views, ideas and concepts presented in articles, and these are the sole responsibility of the author(s);
4. The publishers reserve the right to make textual adjustments and adapt texts to meet with publication standards.
5. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal the right to first publication, with the work simultaneously licensed under the Creative Commons Atribuição NãoComercial 4.0 internacional, which allows the work to be shared with recognized authorship and initial publication in this journal.
6. Authors are allowed to assume additional contracts separately, for non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in this journal (e.g. publish in institutional repository or as a book chapter), with recognition of authorship and initial publication in this journal.
7. Authors are allowed and are encouraged to publish and distribute their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on a personal web page) at any point before or during the editorial process, as this can generate positive effects, as well as increase the impact and citations of the published work (see the effect of Free Access) at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html
• 8. Authors are able to use ORCID is a system of identification for authors. An ORCID identifier is unique to an individual and acts as a persistent digital identifier to ensure that authors (particularly those with relatively common names) can be distinguished and their work properly attributed.












